【数据可视化】基于pyecharts的学生成绩数据集可视化分析
>🧑 博主简介:曾任某智慧城市类企业算法总监,CSDN / 稀土掘金 等平台人工智能领域优质创作者。
>目前在美国市场的物流公司从事高级算法工程师一职,深耕人工智能领域,精通python数据挖掘、可视化、机器学习等,发表过AI相关的专利并多次在AI类比赛中获奖。
---
## 一、引言
在教育研究中,数据可视化是分析学生成绩影响因素的有力工具。本文将利用包含学生考试成绩的数据集,从多个维度进行可视化分析,深入探讨影响学生成绩的因素以及各变量之间的关系。以下分析全部使用 pyecharts 库实现,包含完整 Python 代码,可供读者参考复现。
## 二、数据探索
### 2.1 数据集介绍
数据集包含以下变量:
- **gender**:学生性别
- **race/ethnicity**:学生种族/民族
- **parental level of education**:父母教育水平
- **lunch**:午餐类型
- **test preparation course**:是否参加测试准备课程
- **math score**:数学成绩
- **reading score**:阅读成绩
- **writing score**:写作成绩
### 2.2 数据清洗探索
```python
import pandas as pd
# 加载数据
df = pd.read_csv('student_scores.csv')# 请替换为实际文件路径
# 查看数据基本信息
df.info()
```
从数据基本信息可以看出:
- 数据包含8个维度;
- 性别、种族、父母教育水平等为类别型变量,成绩为数值型变量;
- 数据中存在缺失值,需进一步处理。
## 三、单维度特征可视化
### 3.1 性别分布
```python
from pyecharts.charts import Pie,Bar
from pyecharts import options as opts
def opts_Pie(data_pair,title):
pie = (
Pie(
init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width='1000px', height='800px')
)
.add(series_name="",
data_pair=data_pair,
radius=["30%",'50%'],
center=["38%", "50%"],
label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False, position="center"),
)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(
title=title,
pos_top='2%',
pos_left="29%",
title_textstyle_opts=opts.TextStyleOpts(color='#228be6',font_size=20)
),
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(
is_show=False,
max_=600,
pos_top='70%',
pos_left='20%',
range_color=['blue', 'green', 'yellow', 'red']
),
legend_opts=opts.LegendOpts(is_show=True, pos_right="30%", pos_top="8%",orient="vertical"),
)
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}: {d}%"))
)
return pie
# 性别分布
gender_counts = df['gender'].value_counts().reset_index()
gender_counts.columns = ['gender', 'count']
data_pair = ) for i in range(len(gender_counts))]
pie = opts_Pie(data_pair,'性别分布')
pie.render_notebook()
```
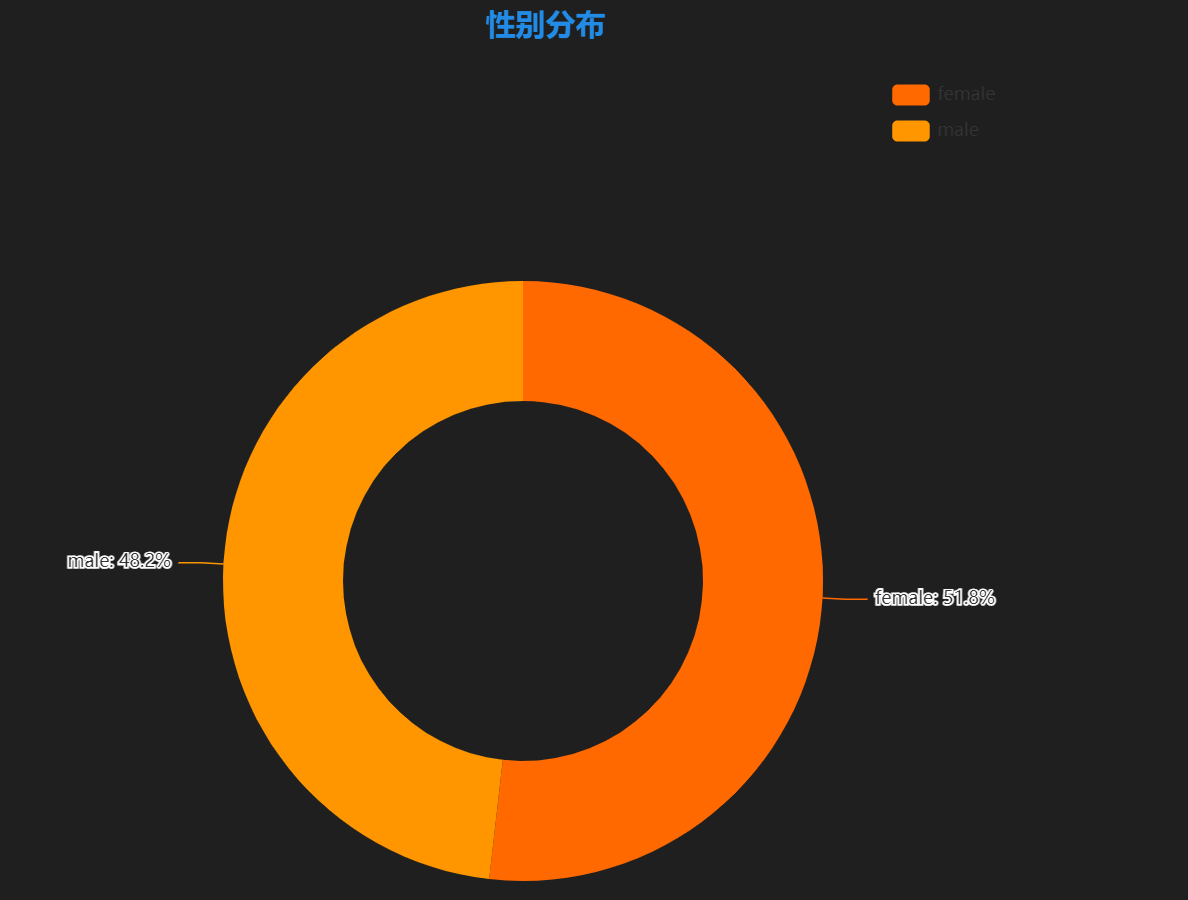
**图表含义**:展示学生性别分布情况。
### 3.2 种族/民族分布
```python
# 种族分布
ethnicity_counts = df['race/ethnicity'].value_counts().reset_index()
ethnicity_counts.columns = ['ethnicity', 'count']
data_pair=) for i in range(len(ethnicity_counts))]
pie = opts_Pie(data_pair,'种族/民族分布')
pie.render_notebook()
```
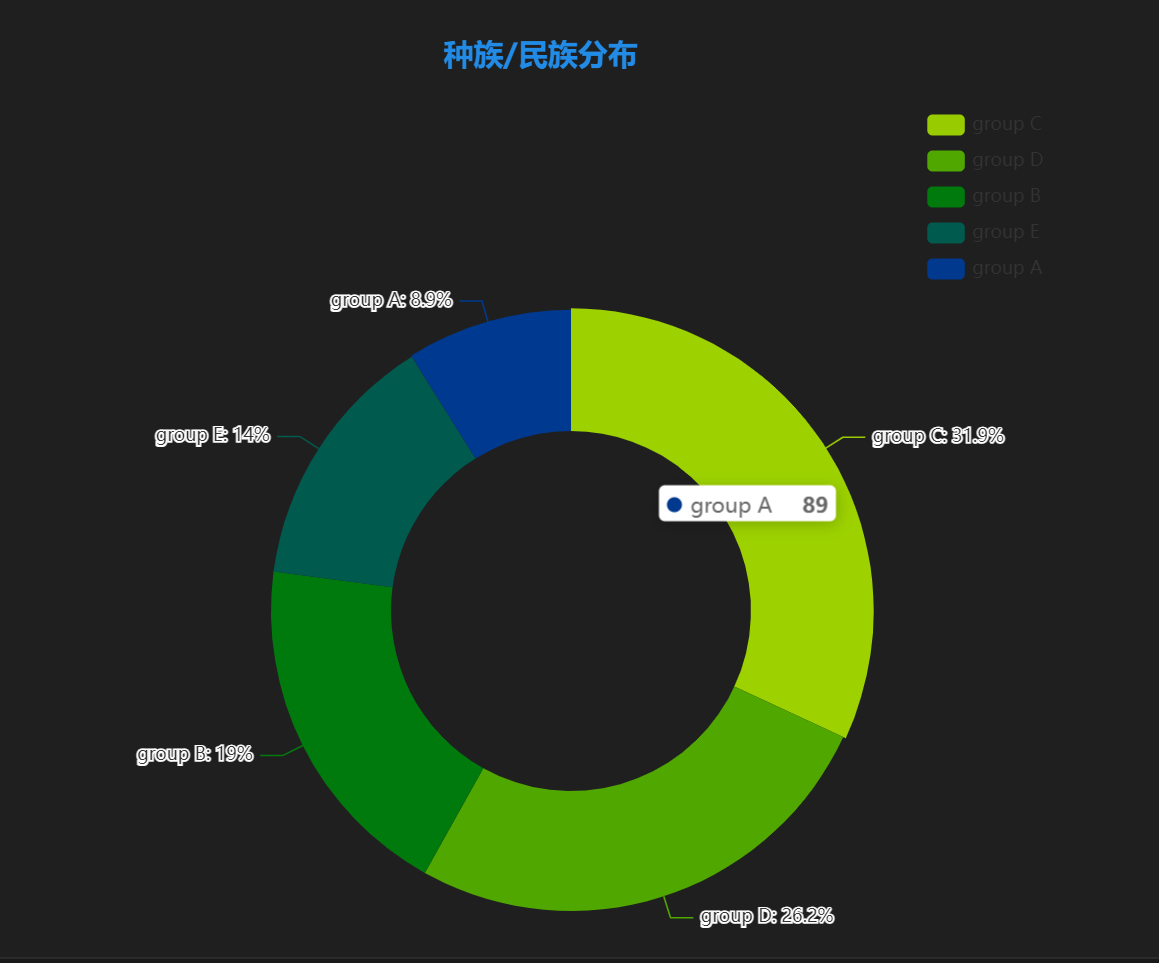
**图表含义**:展示学生种族/民族分布情况。
### 3.3 父母教育水平分布
```python
# 父母教育水平分布
education_counts = df['parental level of education'].value_counts().reset_index()
education_counts.columns = ['education', 'count']
bar_education = Bar()
bar_education.add_xaxis(education_counts['education'].tolist())
bar_education.add_yaxis('人数', education_counts['count'].tolist())
bar_education.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='父母教育水平分布'))
bar_education.render('education_distribution.html')
```
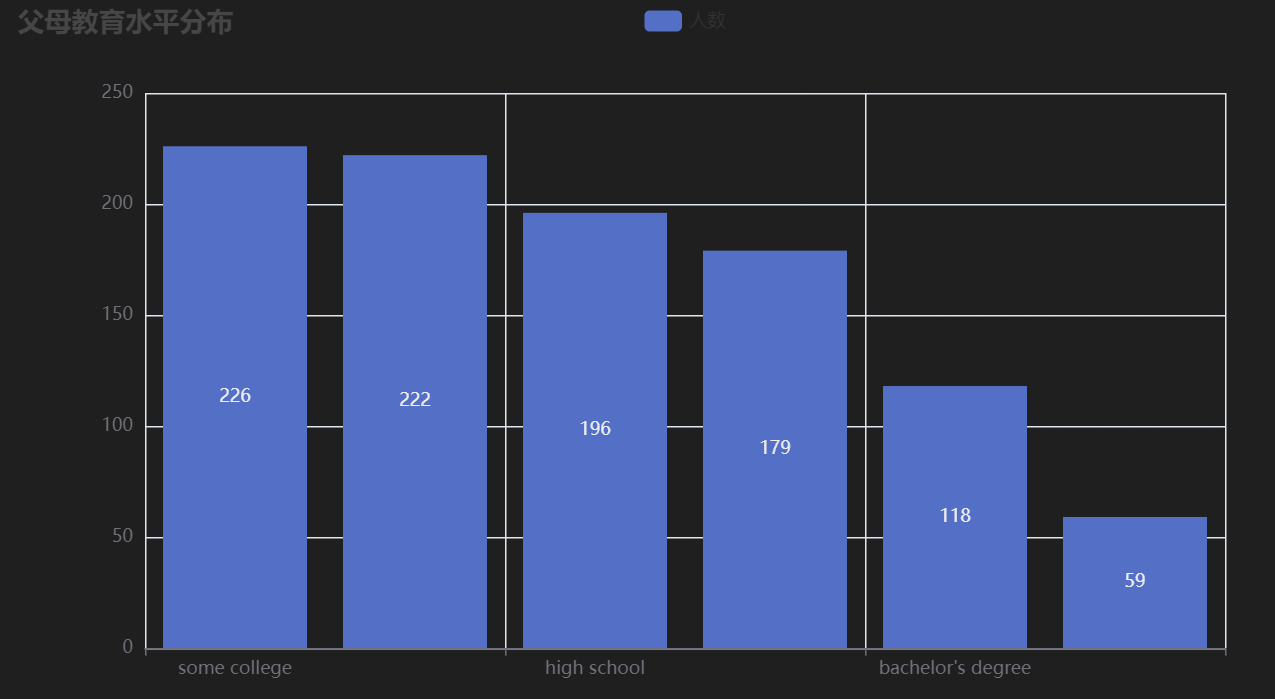
**图表含义**:展示学生父母教育水平分布情况。
### 3.4 午餐类型分布
```python
# 午餐类型分布
lunch_counts = df['lunch'].value_counts().reset_index()
lunch_counts.columns = ['lunch', 'count']
data_pair = ) for i in range(len(lunch_counts))]
poe = opts_Pie(data_pair,'午餐类型分布')
pie.render_notebook()
```
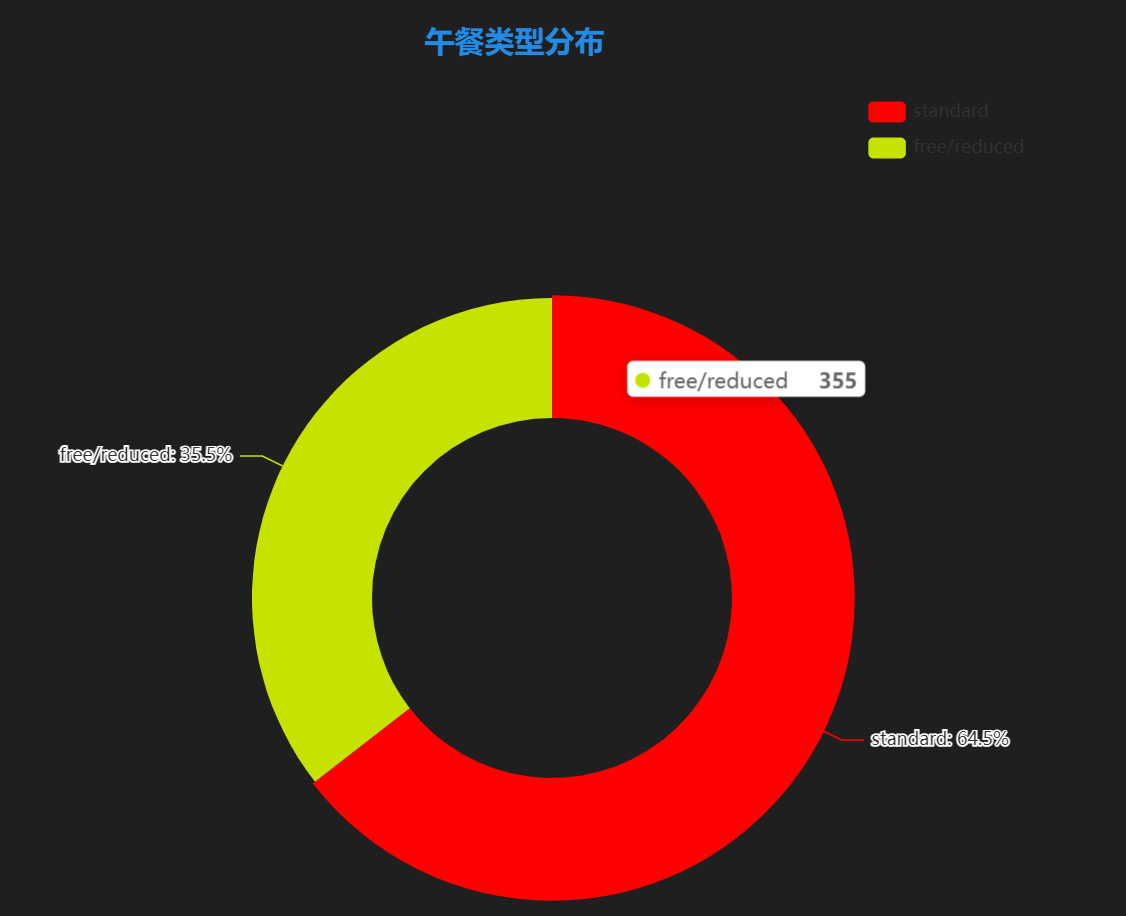
**图表含义**:展示学生午餐类型分布情况。
### 3.5 测试准备课程参与情况
```python
# 测试准备课程参与情况
course_counts = df['test preparation course'].value_counts().reset_index()
course_counts.columns = ['course', 'count']
data_pair = ) for i in range(len(course_counts))]
pie = opts_Pie(data_pair,'测试准备课程参与情况')
pie.render_notebook()
```

**图表含义**:展示学生是否参与测试准备课程的情况。
## 四、各个特征与成绩关系的可视化
### 4.1 性别与成绩关系
```python
from pyecharts.charts import Boxplot
# 性别与成绩关系
def draw_scores_by_gender():
male_scores = df == 'male'][['math score', 'reading score', 'writing score']].values.flatten().tolist()
female_scores = df == 'female'][['math score', 'reading score', 'writing score']].values.flatten().tolist()
boxplot = Boxplot()
boxplot.add_xaxis(['男', '女'])
boxplot.add_yaxis('成绩', )])
boxplot.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='性别与成绩关系'))
boxplot.render('scores_by_gender.html')
draw_scores_by_gender()
```

**图表含义**:展示不同性别学生的成绩分布情况。
### 4.2 种族与成绩关系
```python
# 种族与成绩关系
ethnicity_list = df['race/ethnicity'].unique().tolist()
scores_by_ethnicity = []
for ethnicity in ethnicity_list:
scores = df == ethnicity][['math score', 'reading score', 'writing score']].values.flatten().tolist()
scores_by_ethnicity.append(scores)
boxplot_ethnicity = Boxplot()
boxplot_ethnicity.add_xaxis(ethnicity_list)
boxplot_ethnicity.add_yaxis('成绩', )
boxplot_ethnicity.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='种族与成绩关系'))
boxplot_ethnicity.render('scores_by_ethnicity.html')
```
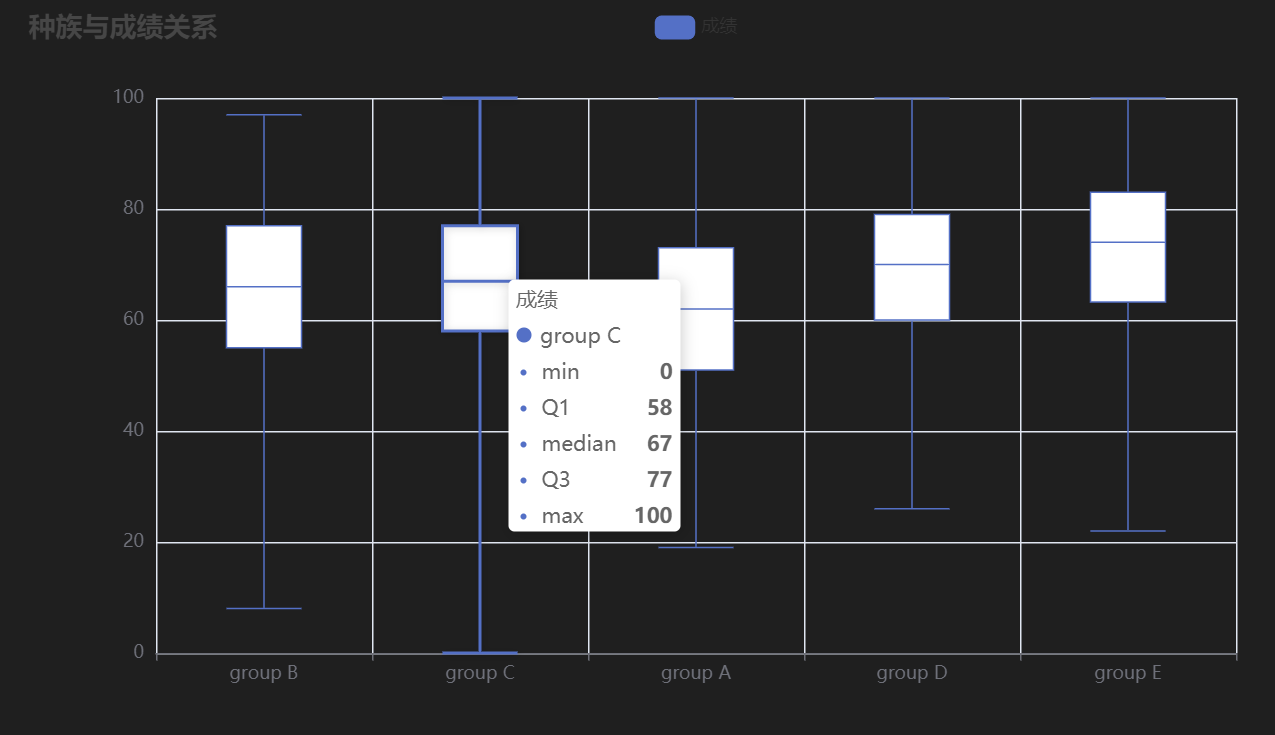
**图表含义**:展示不同种族学生的成绩分布情况。
### 4.3 父母教育水平与成绩关系
```python
# 父母教育水平与成绩关系
education_list = df['parental level of education'].unique().tolist()
scores_by_education = []
for education in education_list:
scores = df == education][['math score', 'reading score', 'writing score']].values.flatten().tolist()
scores_by_education.append(scores)
boxplot_education = Boxplot()
boxplot_education.add_xaxis(education_list)
boxplot_education.add_yaxis('成绩', )
boxplot_education.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='父母教育水平与成绩关系'))
boxplot_education.render('scores_by_education.html')
```
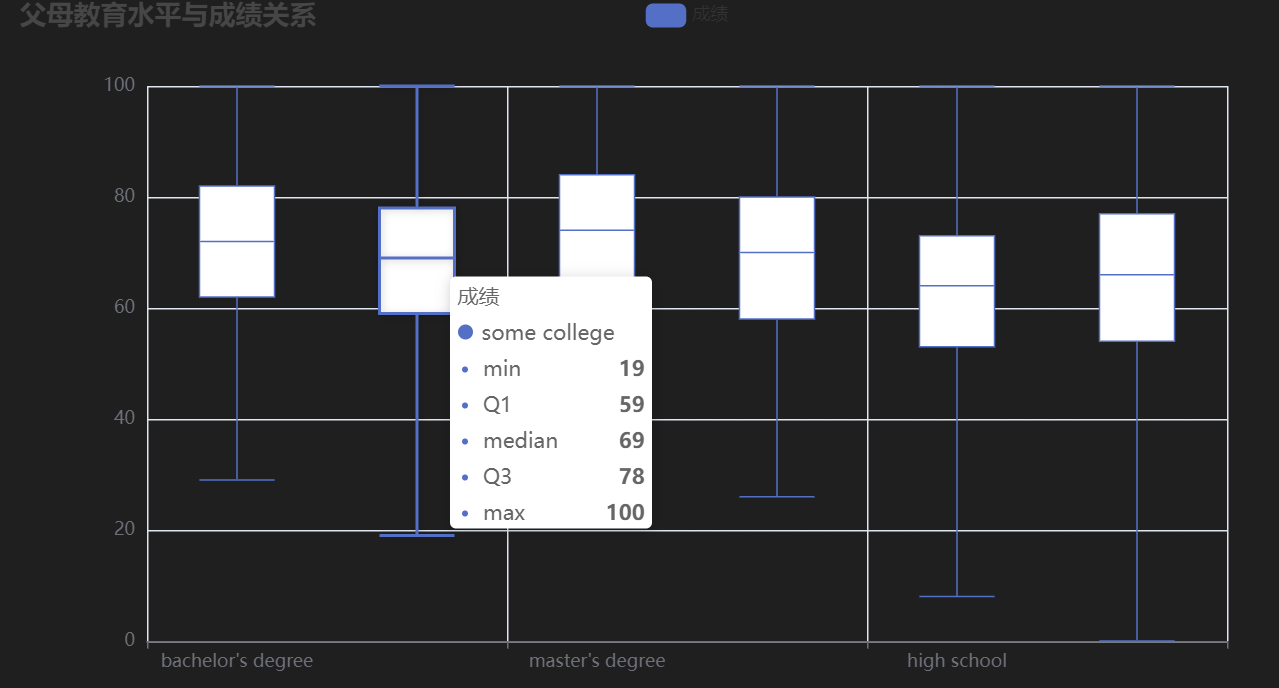
**图表含义**:展示不同父母教育水平学生的成绩分布情况。
### 4.4 午餐类型与成绩关系
```python
# 午餐类型与成绩关系
lunch_list = df['lunch'].unique().tolist()
scores_by_lunch = []
for lunch in lunch_list:
scores = df == lunch][['math score', 'reading score', 'writing score']].values.flatten().tolist()
scores_by_lunch.append(scores)
boxplot_lunch = Boxplot()
boxplot_lunch.add_xaxis(lunch_list)
boxplot_lunch.add_yaxis('成绩', )
boxplot_lunch.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='午餐类型与成绩关系'))
boxplot_lunch.render('scores_by_lunch.html')
```

**图表含义**:展示不同午餐类型学生的成绩分布情况。
### 4.5 测试准备课程与成绩关系
```python
# 测试准备课程与成绩关系
course_list = df['test preparation course'].unique().tolist()
scores_by_course = []
for course in course_list:
scores = df == course][['math score', 'reading score', 'writing score']].values.flatten().tolist()
scores_by_course.append(scores)
boxplot_course = Boxplot()
boxplot_course.add_xaxis(course_list)
boxplot_course.add_yaxis('成绩', )
boxplot_course.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='测试准备课程与成绩关系'))
boxplot_course.render('scores_by_course.html')
```

**图表含义**:展示是否参加测试准备课程学生的成绩分布情况。
### 4.6 数学成绩分布
```python
# 数学成绩分布
# 创建柱状图
bar = Bar()
bar.add_xaxis(list(range(0, 101, 1)))
bar.add_yaxis('数学成绩分布', df['math score'].tolist())
bar.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title='数学成绩分布'),
xaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name='分数段'),
yaxis_opts=opts.AxisOpts(name='人数')
)
bar.render_notebook()
```
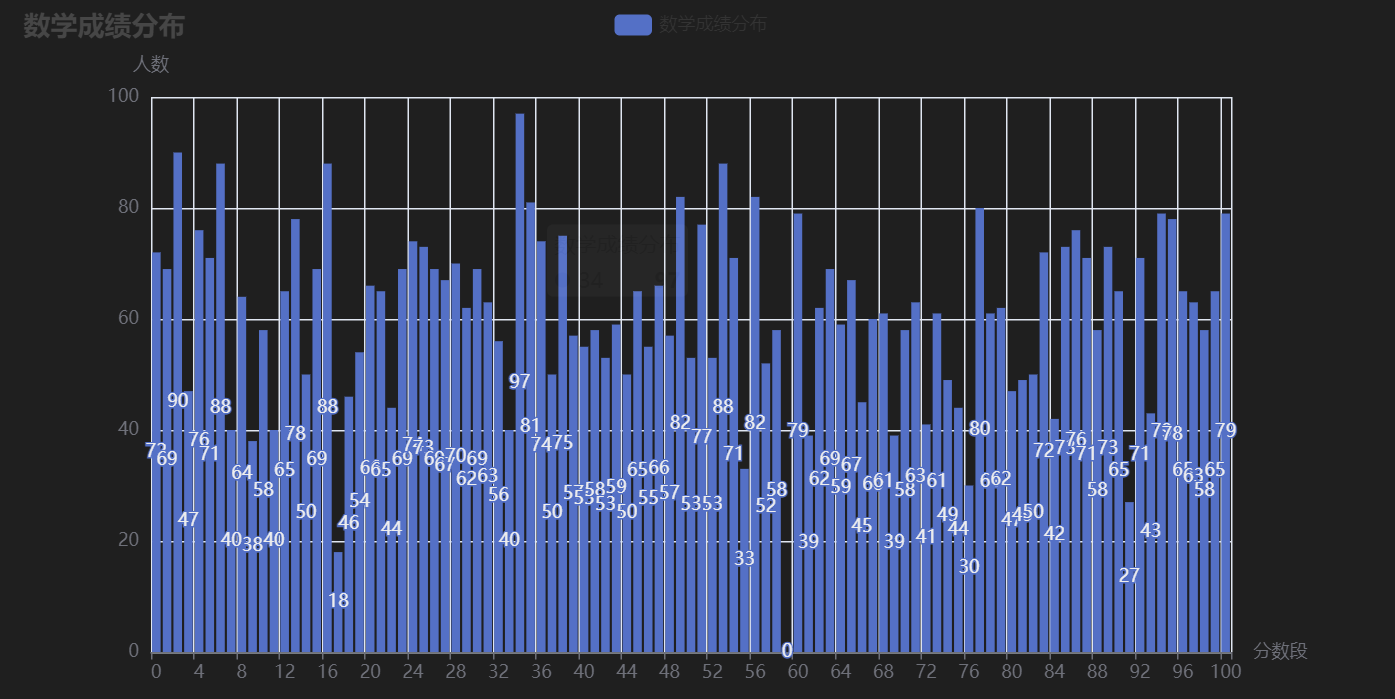
**图表含义**:展示学生成绩的整体分布情况。
从以上可视化结果可以看出:
- **性别与成绩**:男女学生成绩可能存在差异。
- **种族与成绩**:不同种族学生的成绩分布可能存在差异。
- **父母教育水平与成绩**:父母教育水平可能对学生成绩有一定影响。
- **午餐类型与成绩**:午餐类型可能影响学生成绩。
- **测试准备课程与成绩**:参加测试准备课程可能有助于提高学生成绩。
以上分析为理解影响学生成绩的关键因素提供了多维度视角,并揭示了各变量之间的潜在关系,为进一步的教育研究和政策制定提供了数据支持。
如果您还有其他问题或需要进一步的分析,请随时告诉我!
---
如果您在人工智能领域遇到技术难题,或是需要专业支持,无论是技术咨询、项目开发还是个性化解决方案,我都可以为您提供专业服务,如有需要可站内私信或添加下方VX名片(ID:xf982831907)
期待与您一起交流,共同探索AI的更多可能!
页:
[1]